 |
| Agouti vs. black: Moki (left) & Choki (right) |
[Please right-click on highlighted words for Wiki definition.]
Please also read 'Introduction to Mendelian Genetics' if you're not already familiar with Mendel's genetics.
THE AGOUTI & BLACK
According to scientific literature, agouti rats (AA or Aa) have banded hairs that alternate between brown-black and red-yellow pigments. In black (aa) rats, eumelanins are produced continuously, so the hair is evenly black from root to tip.
So here’s the bottom line: your rat’s color is either agouti or black based. Agouti and black are the most basic of all the colors. From there, mutations are made by the influence of color modifying loci.
LOCI OF COAT COLORS
Here are some of the loci that will dictate the phenotype (physical appearance) of a rat.
A (agouti)
Controls the distribution of yellow pigment throughout the coat.
Determines whether the rat will be agouti or black.
B (brown)
Determines whether the coat will be black or brown.
It only affects black.
 |
| Source: Spoiled Ratten Rattery |
 |
| Here's some more chocolate rats for you... Source |
C (albino)
Dilutes yellow and black.
In ‘cc’ both colors are eliminated altogether, producing an albino rat.
In Siamese (chch), yellow pigment is eliminated.
 |
| Pepper, my albino rat, on his 1st birthday (January 9, 2011) |
D (dilute)
Pigment gathers at the base of the hair, and the tips tend to be light, which gives a ticked/silvered effect.
Produces Russian blue agouti and Russian blue.
 |
| This is not a Russian blue, but a victim of cruelty in animal experimentation! Source |
G (grey)
Dilutes black to blue-grey.
 |
| American blue rat. Source |
M (mink)
Dilutes black to gray-brown, but is different from ‘Chocolate’.
 |
| Source: The Dapper Rat |
P (Pink eye)
Dilutes black/brown coat color.
Slightly affects red/yellow pigments.
Causes pink eyes in rats.
Produces amber (agouti) and champagne (black).
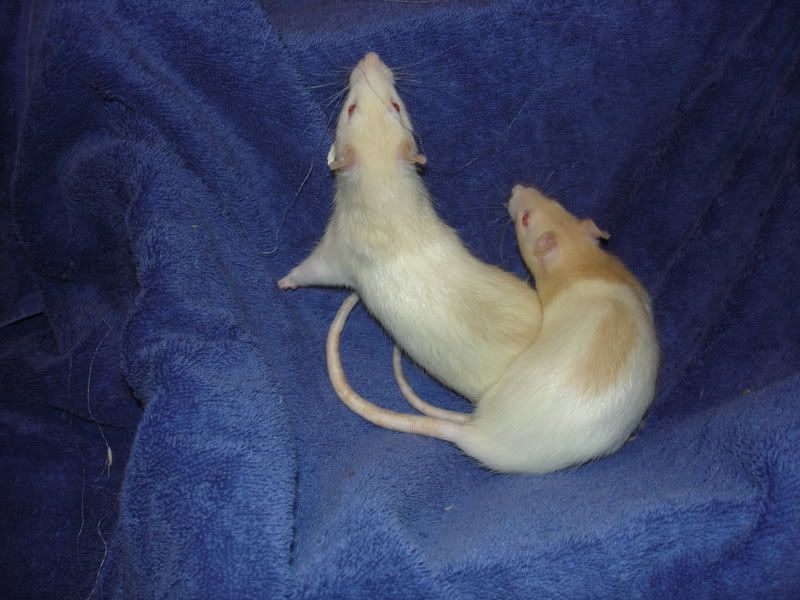 |
| Can you tell which is champagne and amber? Source |
R (Red eye)
It has a lesser intensity of diluting coat color than P.
Causes ruby eyes (eyes that appear black but will show red under light).
Produces fawn (agouti) and beige (black).
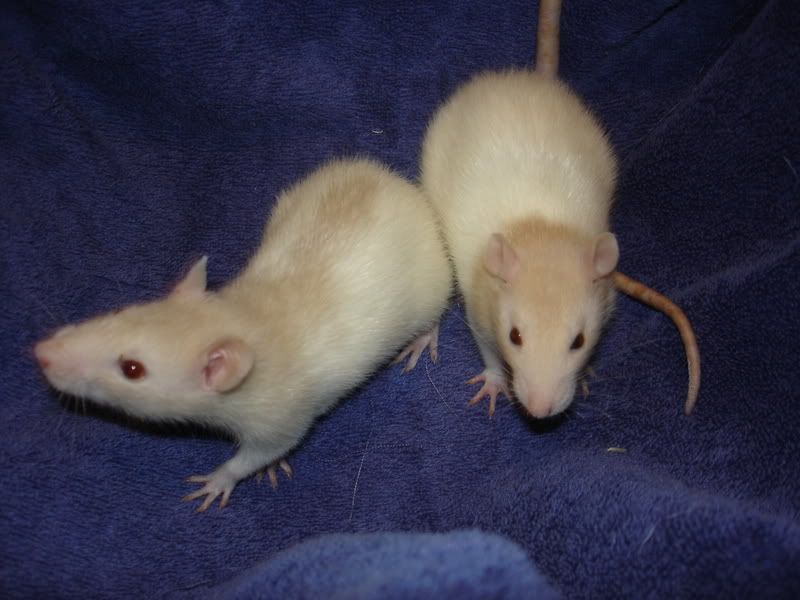 |
| Fawn and beige. Source: Carolina Blue Rattery |
TABLE OF MODIFIED COLORS
How would you know if the color of your rat is agouti or black based?
How could you tell if your rat is fawn or amber? Amber or champagne?
Starting from agouti and black, the basic colors, we can work our way down to other colors by adding modifiers (locus) into the gene of the offspring. I will only include here the simple colors for reference.
 |
| This table created by Rattus Choki |
Bibliography
Mutations in pigment transport and deposition: I. Switching between light and dark on a single hair: black and the agouti gene. Retrieved April 30, 2011 from http://www.ratbehavior.org/CoatColorMutations.htm
Royer, N. Rat genetics Part 1: Loci which regulate coat color. Retrieved April 28, 2011 from http://www.afrma.org/ratgenpart1.htm
Varieties: Body coat/type. Retrieved April 28, 2011 from http://lilratscal.com/variety.htm

No comments :
Post a Comment